Ever wondered how soap transforms from a greasy mess into the delightful bar that cleans up your act? Welcome to the fascinating world of saponification! This magical process, where fats meet lye, creates the sudsy goodness we all know and love. It’s like a chemistry class where the results are both practical and fragrant, making it the perfect blend of science and self-care.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Saponizacao
Saponification involves a chemical reaction that converts fats and oils into soap when combined with lye. This fascinating transformation not only creates a useful product but also illustrates an essential chemical process.
Definition and Process
Saponification occurs when triglycerides in fats interact with a strong alkali. The reaction produces glycerin and fatty acid salts, commonly known as soap. During this process, the alkali breaks down the fats, resulting in a molecular change. Lye, typically sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide, serves as the catalyst. Both cold and hot methods can achieve this reaction, with variations influencing the texture and properties of the final product.
Historical Context
Saponification has roots dating back to ancient civilizations. Babylonians created soap-like substances around 2800 BCE using animal fats and plant ashes. Ancient Egyptians also utilized similar methods for cleaning and personal hygiene. Throughout history, various cultures developed unique techniques, adapting the process with locally available resources. The 19th century marked significant advancements, particularly with the industrial production of soap, enhancing its availability and leading to modern formulations.
The Chemistry of Saponizacao

Saponization involves specific chemical reactions that transform fats into soap, highlighting the role of fatty acids and alkalis in this process.
Role of Fatty Acids
Fatty acids are crucial in saponization. They consist of long hydrocarbon chains attached to a carboxyl group, giving them unique properties. These acids can be saturated or unsaturated, with each type influencing soap’s texture and lather. Common fatty acids include palmitic acid, stearic acid, and oleic acid. When fatty acids react with alkalis, they form fatty acid salts, which constitute the soap itself. Different combinations of fatty acids yield distinct soap qualities, such as hardness and moisturizing effects. Understanding these fatty acids aids in formulating specialized soaps catering to diverse skin types.
Interaction with Alkalis
Alkalis facilitate the saponization reaction by breaking down triglycerides found in fats. Sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide are the most common alkalis used, impacting the soap’s final characteristics. During the reaction, alkali molecules interact with triglycerides, releasing glycerin and forming soap molecules. The choice of alkali influences the soap’s solubility and stability. In hot processes, high temperatures accelerate the reaction, resulting in quicker soap production. Cold processes, however, require more time, allowing for unique textures. Achieving the desired soap properties relies heavily on the specific alkalis used in conjunction with fatty acids.
Applications of Saponizacao
Saponification plays a vital role across various industries and households. Multiple applications showcase its versatility and importance.
Industrial Uses
Industries extensively utilize saponification for producing high-quality soaps and detergents. Specific sectors, like the cosmetics and personal care industry, rely on saponified products for skin health. Various saponified materials serve as emulsifiers, stabilizing agents, and surfactants in formulations. These components enhance the effectiveness of cleaning products, making them more efficient. Additionally, manufacturers focus on developing specialty soaps for specific applications, including industrial cleaners and lubricants.
Household Products
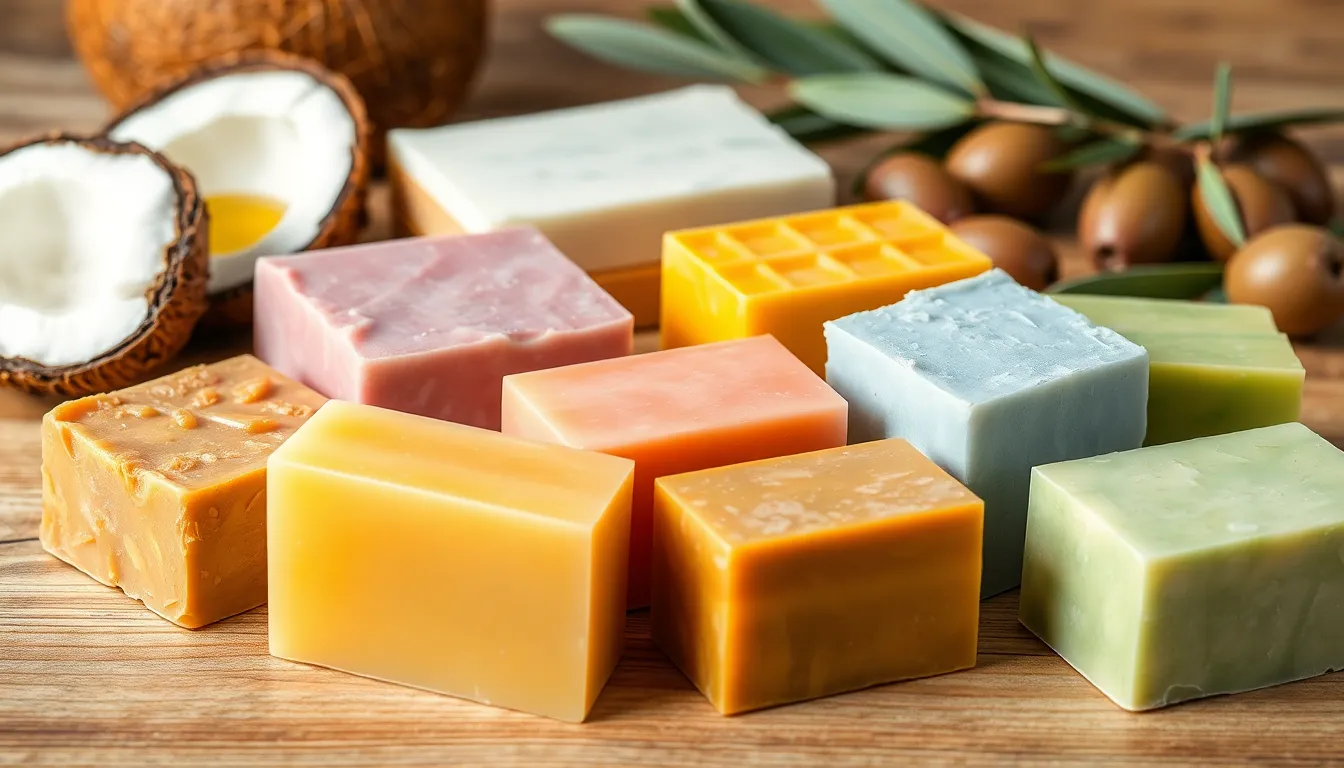
In households, saponification leads to the creation of everyday cleaning products. Soaps derived from saponification provide a multitude of uses, from personal hygiene to laundry cleaning. Many people choose homemade soaps for their natural ingredients and customizable formulations. Various essential oils and additives, such as oatmeal or shea butter, enhance the quality and appeal of these products. Sustainability also drives preferences, as consumers seek eco-friendly options that minimize chemicals while maximizing cleanliness.
Benefits and Challenges
Saponification offers significant advantages and presents certain challenges in the soap-making process. Understanding these aspects helps individuals navigate both benefits and common misconceptions.
Advantages of Saponification
Saponification yields various benefits for consumers and producers. Homemade soaps often contain natural ingredients, providing a healthier option for skin care. Customizable formulations allow users to create products tailored to personal skin types, addressing specific needs effectively. Additionally, it promotes sustainability as many people now choose eco-friendly materials, reducing reliance on commercial products containing harsh chemicals. Industries also benefit, with saponification allowing for the production of high-quality soaps and detergents that enhance personal hygiene and cleaning efficiency.
Common Issues and Misconceptions
Several issues and misconceptions may arise regarding saponification. One prevalent misconception is that all homemade soaps are safer than commercial ones, which isn’t always true; improper measurements of ingredients can result in ineffective or irritating products. Some people believe saponification is an easy process, but it requires careful attention to detail and adherence to safety measures since lye is a caustic substance. Misunderstandings about the final product’s cure time can lead individuals to use soap prematurely, resulting in poor performance. Recognizing these challenges fosters proper practices and enhances the overall experience of soap-making.
Saponification is a fascinating interplay of chemistry and creativity that transforms simple ingredients into essential products for personal care and cleaning. This age-old process not only highlights the art of soap-making but also underscores the importance of understanding the components involved. With a growing preference for natural and eco-friendly options, saponification continues to evolve, catering to diverse needs while promoting sustainability. As individuals explore this craft, they gain insights into the science behind soap, empowering them to create customized solutions that enhance their daily routines. The journey of saponification is not just about making soap; it’s about embracing a healthier lifestyle and reconnecting with the basics of cleanliness.